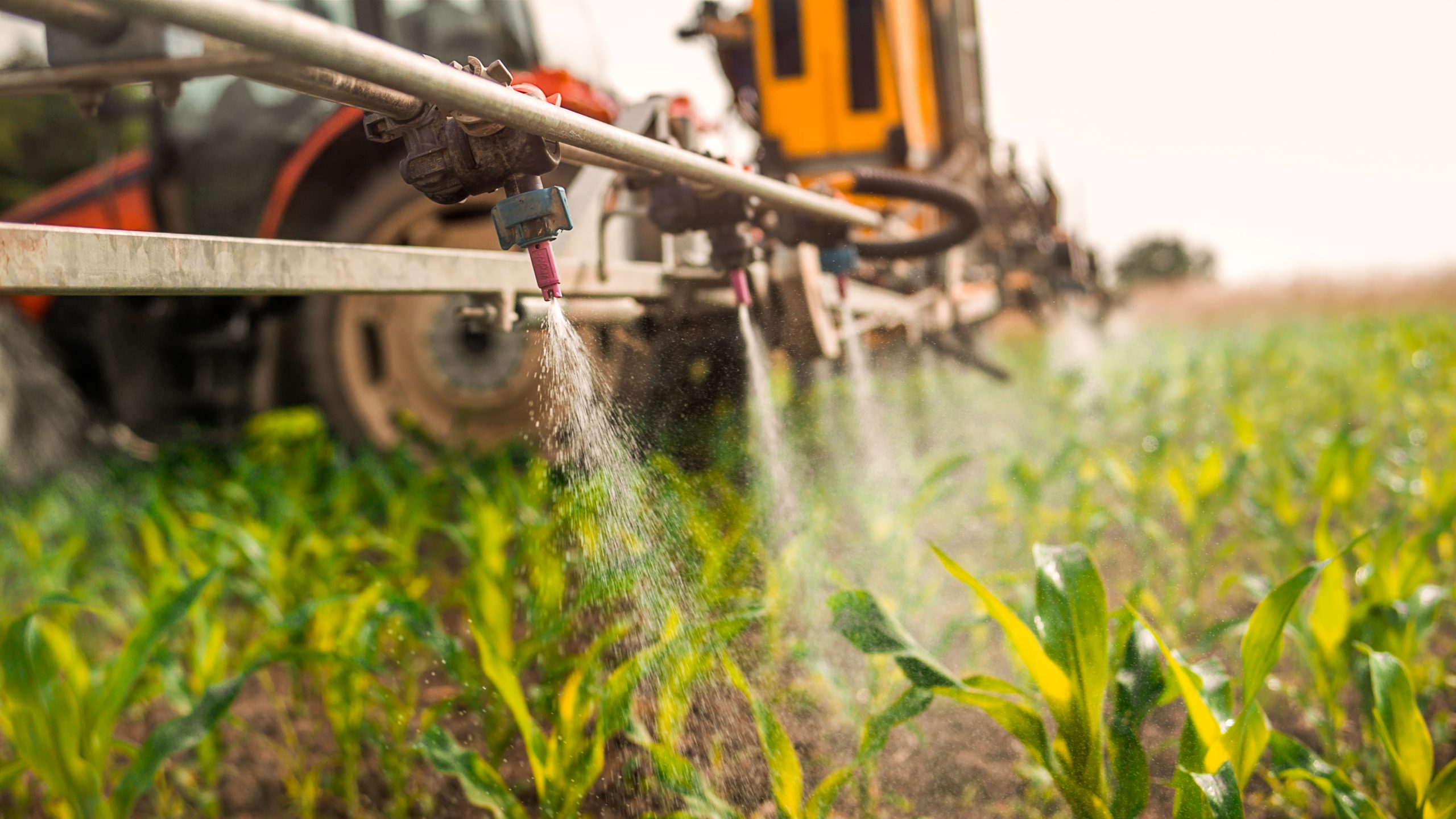

Insect Pest Control: Bifenthrin is effective against a variety of insect pests that can
damage crops, including but not limited to aphids, beetles, caterpillars, thrips, mites,
whiteflies, and leafhoppers. It acts as a neurotoxin, disrupting the insect's nervous system
and leading to paralysis and death.
Fruit and Vegetable Crops: Bifenthrin is commonly used in fruit and vegetable crops such as
apples, citrus fruits, tomatoes, peppers, cucurbits (e.g., cucumbers, squash, melons),
strawberries, and leafy greens. It protects these crops from chewing and sucking pests that
can cause yield losses and quality degradation.
Field Crops: Bifenthrin is applied to field crops such as corn, soybeans, cotton, wheat,
rice, and potatoes to control pests like corn earworms, armyworms, soybean aphids, spider
mites, potato beetles, and bollworms. It helps maintain crop health and maximize yields by
reducing pest damage.
Tree and Vine Crops: Bifenthrin is used in tree fruit orchards (e.g., apples, peaches,
cherries) and vineyards (e.g., grapes) to manage pests such as codling moths, apple maggots,
grapevine moths, and leafhoppers. It protects trees and vines from insect damage during the
growing season.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Bifenthrin is part of integrated pest management
strategies that combine biological, cultural, and chemical control methods. It is often used
judiciously and in rotation with other insecticides to minimize pest resistance and
environmental impact.
Application Methods: Bifenthrin can be applied as foliar sprays, soil treatments, seed
treatments, or through irrigation systems (chemigation). Application rates and timings are
determined based on pest pressure, crop stage, weather conditions, and label
recommendations.

